by
Penn Dental Medicine’s Michel Koo, Co-Director and Co-Founder of the Center for Innovation & Precision Dentistry (CiPD), was among a panel of researchers, engineers, and business founders invited to be part of a recent Trailblazers with Walter Isaacson Podcast titled “Dentistry: An Oral History of Disruption.”
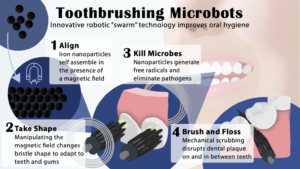
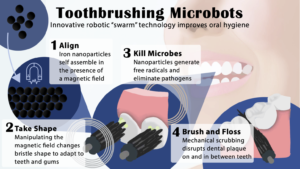
Koo shared findings from one of his recent studies conducted in collaboration with Penn Engineering, which showed that a shapeshifting robotic microswarm can brush and floss teeth.
“Routine oral care is cumbersome and can pose challenges for many people, especially those who have a hard time cleaning their teeth” says Koo. “You have to brush your teeth, then floss your teeth, then rinse your mouth; it’s a manual, multistep process. The big innovation here is that the robotics system can do all three in a single, hands-free, automated way.”
The building blocks of these microrobots are iron oxide nanoparticles that have both catalytic and magnetic activity. Using a magnetic field, researchers could direct their motion and configuration to form either bristlelike structures that sweep away dental plaque from the broad surfaces of teeth, or elongated strings that can slip between teeth like a length of floss.
“Nanoparticles can be shaped and controlled with magnetic fields in surprising ways,” says Edward Steager, a senior research investigator at Penn Engineering and co-corresponding author. “We form bristles that can extend, sweep, and even transfer back and forth across a space, much like flossing. The way it works is similar to how a robotic arm might reach out and clean a surface. The system can be programmed to do the nanoparticle assembly and motion control automatically.”
Listen to “Dentistry: An Oral History of Disruption” to learn more about Toothbrushing Microbots.
This story originally appeared in Penn Engineering Today.