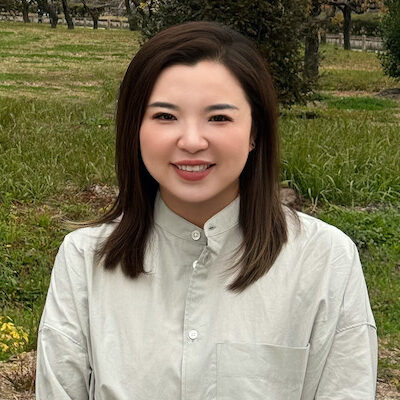
Sherry (Xue) Gao, Presidential Penn Compact Associate Professor in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), always knew she had a future in the lab. “I grew up in China, and when I was little, maybe six or seven,” she recalls, “my teacher asked me, ‘What do you want to be when you grow up?’ I said, ‘I want to be a scientist!’”
Neither of her parents had studied beyond high school; when Gao finished her training as a chemical engineer, she became the first person in her family to graduate from college. “One of my greatest motivations is to help first-generation college students,” Gao says.
Now, as the newest faculty member in CBE, Gao is prepared to do just that: support the next generation of chemical engineers, while also conducting groundbreaking research in the development of small molecules to edit genes, pushing the boundaries of precision medicine.
The Presidential Penn Compact Professorships were created by former Penn President Amy Gutmann specifically to recruit and support faculty like Gao: transformative leaders working at the intersection of multiple fields with “a yen for collaboration,” as Gutmann told the Penn Gazette in 2021.
Gao joins Penn Engineering from Rice University, where she collected numerous accolades, including the 2024 BMES-CMBE Rising Star Award, a 2022 NSF CAREER Award, the 2022 Outstanding Young Faculty at Rice School of Engineering Award and the 2020 NIH MIRA R35 Award.
As a member of the Center for Precision Engineering for Health (CPE4H), Gao will partner with colleagues from across the School to develop technologies that bridge disciplines, all in the interest of advancing health care. “We are very excited to have Sherry as a new member of the Center,” says Daniel Hammer, Alfred G. and Meta A. Ennis Professor and inaugural Director of CPE4H. “Gene editing is an important new tool that can precisely alter cell behavior by deleting or redirecting cell pathways, as well as enhancing and suppressing gene expression. She will have significant interactions with other members of the Center, such as Mike Mitchell and myself, as well as the broader Penn community, especially with the CAR therapists.”
Read the full story in Penn Engineering Today.
Since this story was originally published in March 2024, Sherry Gao now holds a secondary appointment in Bioengineering, effective July 1, 2024.
Daniel Hammer and Michael Mitchell both hold primary appointments in Bioengineering.




 A research team led by engineers at the
A research team led by engineers at the