by Erica K. Brockmeier
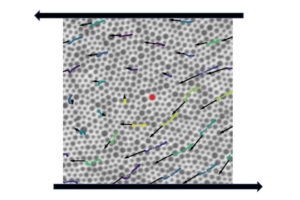
New research published in Nature Physics details the relationship between a disordered material’s individual particle arrangement and how it reacts to external stressors. The study also found that these materials have “memory” that can be used to predict how and when they will flow. The study was led by Larry Galloway, a Ph.D. student in the lab of Paulo Arratia, and Xiaoguang Ma, a former postdoc in the lab of Arjun Yodh, in collaboration with researchers in the labs of Douglas Jerolmack and Celia Reina.
A disordered material is randomly arranged at the particle-scale, e.g. atoms or grains, instead of being systematically distributed—think of a pile of sand instead of a neatly stacked brick wall. Researchers in the Arratia lab are studying this class of materials as part of Penn’s Materials Research Science & Engineering Center, where one of the program’s focuses is on understanding the organization and proliferation of particle-scale rearrangements in disordered, amorphous materials.
The key question in this study was whether one could observe the structure of a disordered material and have some indication as to how stable it is or when it might begin to break apart. This is known as the yield point, or when the material “flows” and begins to move in response to external forces. “For example, if you look at the grains of a sand castle and how they are arranged, can I tell you whether the wind can blow it over or if it has to be hit hard to fall over?” says Arratia. “We want to know, just by looking at the way the particles are arranged, if we can say anything about the way they’re going to flow or if they are going to flow at all.”
While it has been known that individual particle distribution influences yield point, or flow, in disordered materials, it has been challenging to study this phenomenon since the field lacks ways to “quantify” disorder in such materials. To address this challenge, the researchers collaborated with colleagues from across campus to combine expertise across the fields of experimentation, theory, and simulations.
Read the full story in Penn Today.
The authors are Larry Galloway, Erin Teich, Christoph Kammer, Ian Graham, Celia Reina, Douglas Jerolmack, Arjun Yodh, and Paulo Arratia from Penn; Xiaoguang Ma, previously a postdoc at Penn and now at the Southern University of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, China; and Nathan Keim, previously a postdoc at Penn and now at Pennsylvania State University.
Arjun Yodh is the James M. Skinner Professor of Science in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in Penn’s School of Arts & Sciences and a member of the Penn Bioengineering Graduate Group.
Paulo Arratia is a professor in the departments of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics and Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of Pennsylvania.
Douglas Jerolmack is a professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Science in Penn’s School of Arts & Sciences and in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics at Penn Engineering.
Celia Reina is the William K. Gemmill Term Assistant Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics at Penn Engineering.
