by Erica Moser

As a neuroscientist surveying the landscape of generative AI—artificial intelligence capable of generating text, images, or other media—Konrad Kording cites two potential directions forward: One is the “weird future” of political use and manipulation, and the other is the “power tool direction,” where people use ChatGPT to get information as they would use a drill to build furniture.
“I’m not sure which of those two directions we’re going but I think a lot of the AI people are working to move us into the power tool direction,” says Kording, a Penn Integrates Knowledge (PIK) University professor with appointments in the Perelman School of Medicine and School of Engineering and Applied Science. Reflecting on how generative AI is shifting the paradigm of science as a discipline, Kording said he thinks “it will push science as a whole into a much more collaborative direction,” though he has concerns about ChatGPT’s blind spots.
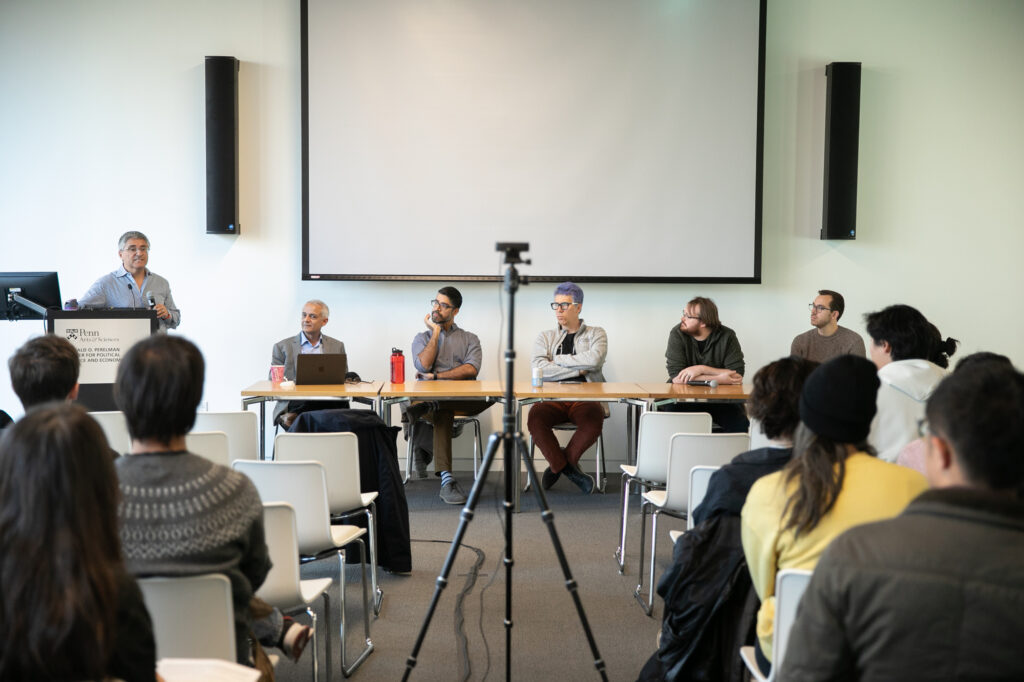
Kording joined three University of Pennsylvania researchers from the chemistry, political science, and psychology departments sharing their perspectives in the recent panel “ChatGPT turns one: How is generative AI reshaping science?” PIK Professor René Vidal opened the event, which was hosted by the School of Arts & Sciences’ Data Driven Discovery Initiative (DDDI), and Bhuvnesh Jain, physics and astronomy professor and co-faculty director of DDDI, moderated the discussion.
“Generative AI is moving so rapidly that even if it’s a snapshot, it will be very interesting for all of us to get that snapshot from these wonderful experts,” Jain said. OpenAI launched ChatGPT, a large language model (LLM)-based chatbot, on Nov. 30, 2022, and it rapidly ascended to ubiquity in news reports, faculty discussions, and research papers. Colin Twomey, interim executive director of DDDI, told Penn Today that it’s an open question as to how it will change the landscape of scientific research, and the` idea of the event was to solicit colleagues’ opinions on interesting directions in their fields.
Read the full story in Penn Today.
Konrad Paul Kording is Nathan Francis Mossell University Professor in Bioengineering and Computer and Information Science in Penn Engineering and in Neuroscience in the Perelman School of Medicine.


 David Brainard is the RRL Professor of Psychology, director of the
David Brainard is the RRL Professor of Psychology, director of the