by Kelsey Geesler

When we hear about gut bacteria, we may think about probiotics and supplements marketed to help with digestion, about how taking antibiotics might affect our intestinal tract, or perhaps about trendy diets that aim to improve gut health.
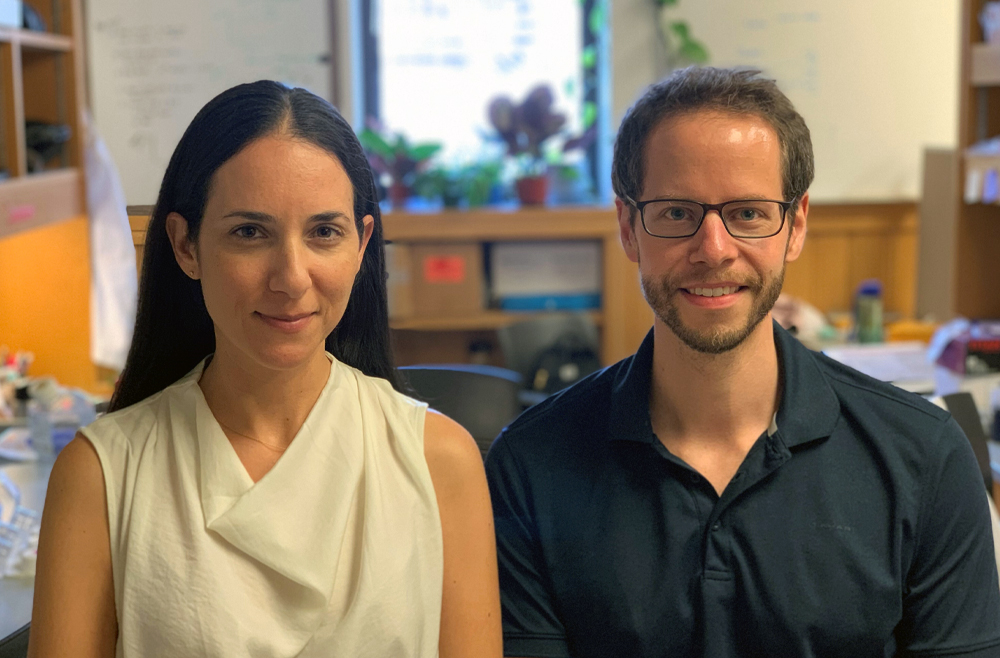
But two researchers at Penn Medicine think that understanding the microbiome, the entirety of microbial organisms associated with the human body, might be the key to deciphering the fundamental mechanisms that make our bodies work. They think these microbes may work like a call center switchboard, making connections to help different organs, biological systems, and the brain communicate. Maayan Levy, and Christoph Thaiss, both assistant professors of microbiology at the Perelman School of Medicine, argue that the microbiome is instrumental to revealing how signals from the gastrointestinal tract are received by the rest of the body—which may hold the key to understanding inter-organ communication in general. Perelman School of Medicine’s Maayan Levy, and Christoph Thaiss. (Image: Courtesy of Penn Medicine News)
While the gut sends signals to all parts of the body to initiate various biological processes, the mechanisms underlying this communication—and communication between different organs involved in these processes—is relatively unknown.
“The more we learn about the role the microbiome plays in a wide range of diseases— from cancer to neurodegenerative diseases to inflammatory diseases—the more important it becomes to understand what exactly its role is,” says Thaiss. “And hopefully once we understand how it works, we can use the microbiome to treat these diseases.”
Levy and Thaiss joined the faculty at Penn Medicine after completing their graduate studies in 2018. Here, they continue to investigate the role of the microbiome in various biological processes.
In his lab, Thaiss focuses on the impact of the microbiome on the brain. He recently identified species of gut-dwelling bacteria that activate nerves in the gut to promote the desire to exercise. Most recently, Thaiss published a study that identified the cells that communicate psychological stress signals from the brain to the gastrointestinal tract, and cause symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease.
Meanwhile, in her lab, Levy examines how the microbiome influences the development of diseases, like cancer, and other conditions throughout the body.
A recent publication authored by Levy suggested that the ketogenic diet (high fat, low carbohydrate) causes the production of a metabolite called beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), that suppresses colorectal cancer in small animal models.
Now, Levy is collaborating with Bryson Katona, an assistant professor of Medicine in the division of gastroenterology who specializes in gastrointestinal cancers, to investigate whether BHB has the same effect in patients with Lynch syndrome, which causes individuals to have a genetic predisposition to many different kinds of cancer, including colon cancer. These efforts are part of a growing emphasis at Penn on finding methods to intercept cancer in its earliest stages.
“It’s remarkable that we were able to quickly take the findings from our animal models and rapidly design a clinical trial,” Levy says. “One of the most exciting aspects of our work is not only making discoveries about how our bodies work on a biological level, but then being able to work with the world’s leading clinical experts to translate these discoveries into therapies for patients.”
Further, studies led by Levy and Thaiss often utilize human samples and data from the Penn Medicine BioBank, to validate animal model findings in the tissue of human patients suffering from the diseases which they are investigating.
While Levy and Thaiss pursue different research interests with their labs, they also collaborate often, building on their previous research into what the microbiome does, and its role in the biological processes that keep us healthy. Their long-term goal is to learn about the mechanisms by which the gastrointestinal tract influences disease processes in other organs to treat various diseases of the body using the gastrointestinal tract as a noninvasive entry point to the body.
“Some of the most common and devastating diseases in humans—like cancer or neurodegeneration—are difficult to treat because they are no existing therapies that can reach the brain,” says Thaiss. “If we can understand how the gastrointestinal tract interacts with other organs in the body, including the brain, we might be able to develop treatments that ‘send messages’ to these organs through the body’s natural communication pathways.”
“Obviously there is a lot more basic biology to be uncovered before we get there,” adds Levy. “Most importantly, we want to map all the different routes by which the gastrointestinal tract interacts with the body, and how that communication happens.”
Read the full story in Penn Medicine News.
Christopher Thaiss is Assistant Professor in Microbiology in the Perelman School of Medicine. He is a member of the Penn Bioengineering Graduate Group.

 A research team led by engineers at the
A research team led by engineers at the