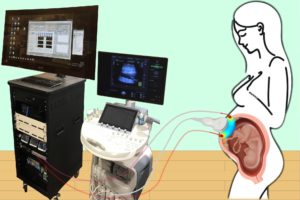
A study published in Nature Biomedical Engineering details a novel method for imaging the placenta in pregnant patients as well as the results of a pilot clinical study. By combining optical measurements with ultrasound, the findings show how oxygen levels can be monitored noninvasively and provides a new way to generate a better understanding of this complex, crucial organ. This research was the result of a collaboration of the groups of the University of Pennsylvania’s Arjun Yodh and Nadav Schwartz with colleagues from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and was led by postdoc Lin Wang.
Schwartz describes the placenta as the “engine” of pregnancy, an organ that plays a crucial role in delivering nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. Placental dysfunction can lead to complications such as fetal growth restriction, preeclampsia, and stillbirth. To increase knowledge about this crucial organ, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development launched the Human Placenta Project in 2014. One focus of the program is to develop tools to assess human placental structure and function in real time, including optical devices.
For three years, the researchers optimized the design of their instrument and tested it in preclinical settings. The process involved integrating optical fibers with ultrasound probes, exploring various ultrasound transducers, and improving the multimodal technology so that measurements were stable, accurate, and reproducible while collecting data at the bedside. The resulting instrumentation now enables researchers to study the anatomy of the placenta while also collecting detailed functional information about placenta blood flow and oxygenation, capabilities that existing commercially devices do not have, the researchers say.
Because the placenta is located far below the body’s surface, one of the key technical challenges addressed by Wang, a postdoc in Yodh’s lab, was reducing background noise in the opto-electronic system. Light is scattered and absorbed when it travels through thick tissues, Yodh says, and the key for success was to reduce background interference so that the small amount of light that penetrates deep into the placenta and then returns is still large enough for a high-quality measurement.
“We’re sending a light signal that goes through the same deep tissues as the ultrasound. The extremely small amount of light that returns to the surface probe is then used to accurately assess tissue properties, which is only possible with very stable lasers, optics, and detectors,” says Yodh. “Lin had to overcome many barriers to improve the signal-to-noise ratio to the point where we trusted our data.”
Read the full story in Penn Today.
The authors are Lin Wang, Jeffrey M. Cochran, Kenneth Abramson, Lian He, Venki Kavuri, Samuel Parry, Arjun G. Yodh, and Nadav Schwartz from Penn; Tiffany Ko, Wesley B. Baker, and Rebecca L. Linn from the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and David R. Busch, previously a research associate at Penn and now at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School.
Arjun Yodh is the James M. Skinner Professor of Science in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in the School of Arts & Sciences at the University of Pennsylvania. He is a member of the Penn Bioengineering Graduate Group.
Nadav Schwartz is an Associate Professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Penn’s Perelman School of Medicine.
Lin Wang is a postdoc in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in Penn’s School of Arts & Sciences.
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health grants F31HD085731, R01NS113945, R01NS060653, P41EB015893, P41EB015893, T32HL007915, and U01HD087180.