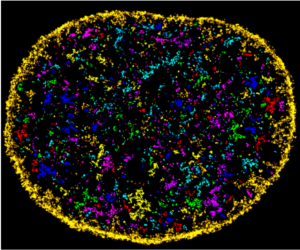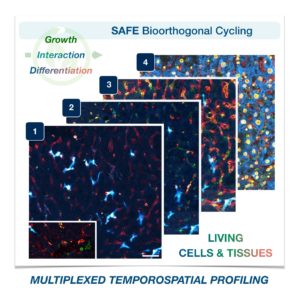
Cells in complex organisms undergo frequent changes, and researchers have struggled to monitor these changes and create a comprehensive profile for living cells and tissues. Historically researchers have been limited to only 3-5 markers due to spectral overlaps in fluorescence microscopy, an essential tool required for imaging cells. With only this small handful of markers, it is difficult to monitor protein expressions of live cells and a comprehensive profile of cellular dynamics cannot be created. However, a new study in Nature Biotechnology addresses these limitations by demonstrating a new method for comprehensive profiling of living cells.

Jina Ko, Assistant Professor in Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and in Pathology and Laboratory Medicine in the Perelman School of Medicine, conducted postdoctoral research at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Wyss Institute at Harvard University, and the work for this study was done under the supervision of Jonathan Carlson M.D., Ph.D. and Ralph Weissleder M.D., Ph.D. of MGH. Ko’s lab at Penn develops novel technologies using bioengineering, molecular biology, and chemistry to address diagnostic challenges for precision medicine.
To address these limitations in microscopy, the team developed a new chemistry tool which was highly gentle to cells. This “scission-accelerated fluorophore exchange (or SAFE)” method utilizes “click” chemistry, a type of chemistry that follows examples found in nature to create fast and simple reactions. This new SAFE method functions with non-toxic conditions to living cells and tissues, whereas previous methods have used harsh chemicals that would strip off fluorophores and consequently would not work with living cells and tissues.
With the development of SAFE, the authors demonstrated that researchers can now effectively perform multiple cycles of cell profiling and can monitor cellular changes over the course of their observations. Instead of the previous limitation of 3-5 markers total, SAFE allows for many more cycles and can keep track of almost as many markers as the researcher wants. One can now stain cells and quench/release fluorophores and repeat the cycle multiple times for multiplexing on living cells. Each cycle can profile 3 markers, and so someone interested in profiling 15 markers could easily perform 5 cycles to achieve this much more comprehensive cell profile. With this breakthrough in more detailed imaging of cells, SAFE demonstrates broad applicability for allowing researchers to better investigate the physiologic dynamics in living systems.
Read the paper, “Spatiotemporal multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging of living cells and tissues with bioorthogonal cycling of fluorescent probes,” in Nature Biotechnology.
This study was supported by the Schmidt Science Fellows in Partnership with the Rhodes Trust and National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (K99CA256353).