We hope you will join us for the 2023 Herman P. Schwan Distinguished Lecture by Dr. Dorin Comaniciu, hosted by the Department of Bioengineering.
Wednesday, December 13, 2023
1:00 PM ET
Location: Wu & Chen Auditorium (Levine 101)
The lecture and Q&A will be followed by a light reception in Levine Lobby.
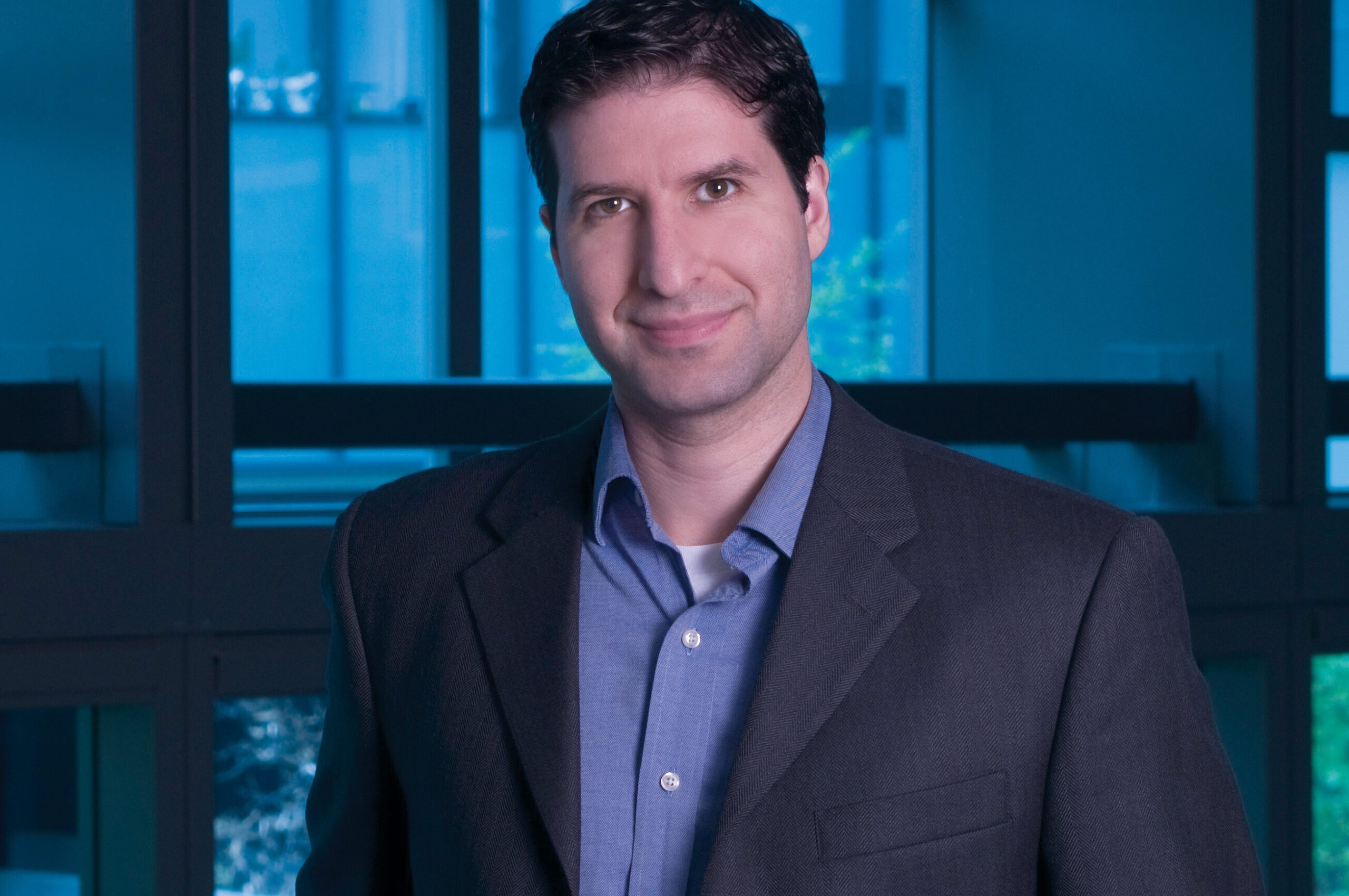
Speaker: Dorin Comaniciu, Ph.D.
Senior Vice President
Artificial Intelligence and Digital Innovations
Siemens Healthineers
About Dorin Comaniciu:
Dr. Comaniciu serves as Senior Vice President for Artificial Intelligence and Digital Innovation at Siemens Healthineers. His scientific contributions to machine intelligence and computational imaging have translated to multiple clinical products focused on improving the quality of care, specifically in the fields of diagnostic imaging, image-guided therapy, and precision medicine.
Comaniciu is a member of the National Academy of Medicine, the Romanian Academy, and a Top Innovator of Siemens. He is a Fellow of the IEEE, ACM, MICCAI Society, and AIMBE, and a recipient of the IEEE Longuet-Higgins Prize for fundamental contributions to computer vision. Recent recognition of his work includes an honorary doctorate from Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg.
He has co-authored 550 granted patents and 350 peer-reviewed publications that have received 61,000 citations, with an h-index of 102, in the areas of machine intelligence, medical imaging, and precision medicine.
A graduate of University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School, Comaniciu received a doctorate in electrical and computer engineering from Rutgers University and a doctorate in electronics and telecommunications from Polytechnic University of Bucharest.
He is an advocate for technological innovations that save and enhance lives, addressing critical issues in global health.
About the Schwan Lecture:
The Herman P. Schwan Distinguished Lecture is in honor of one of the founding members of the Department of Bioengineering, who emigrated from Germany after World War II and helped create the field of bioengineering in the US. It recognizes people with a similar transformative impact on the field of bioengineering.