
One of the most important but least understood aspects of healing is cell migration, or the process of cells moving from one part of the body to another. “If you are an ambulance out in the woods,” says Karen Xu, an M.D/Ph.D. student in Medicine and Bioengineering, “and there are no paths for you to move forward, it will be a lot harder for you to get to a site that needs you.”
Earlier this year, Xu co-authored a paper in Nature Communications describing a new cue to help cells get to where they need to go: a material made chiefly of hyaluronic acid and gelatin, two gooey substances commonly found outside cells in joints and connective tissue.
“Hundreds of thousands of people tear their meniscus every year,” says Robert Mauck, Mary Black Ralston Professor in Orthopaedic Surgery in Penn Medicine and Professor in Bioengineering at Penn Engineering and one of Xu’s advisors, as well as a senior author on the paper. “This material could potentially speed up their recovery.”
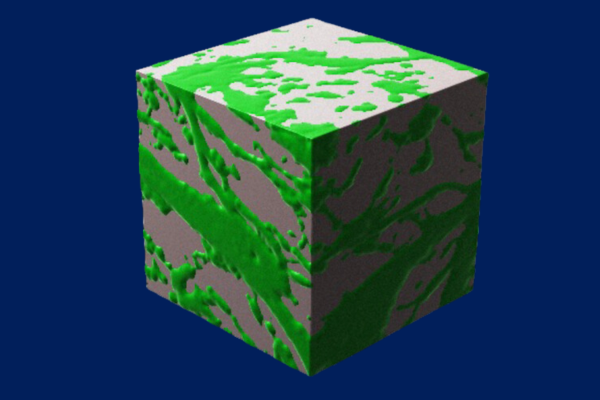
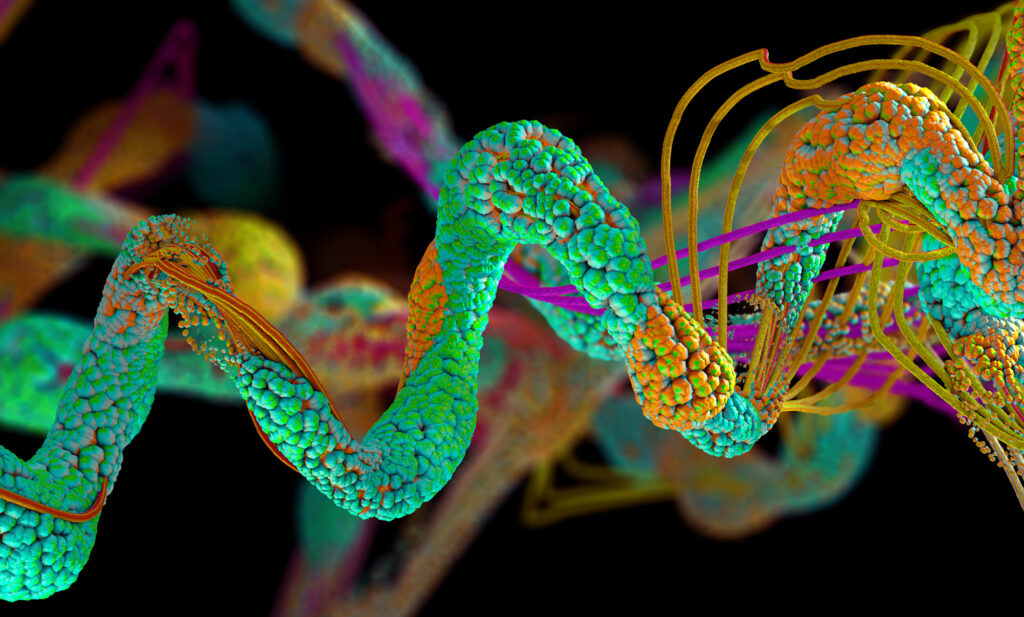
What makes the material — known as a hydrogel due to its blend of gelatinous matter and water — unique is that the combination of hyaluronic acid and gelatin forms a complex network of paths, providing cells many different ways to travel between two points.
This property is known as bicontinuity, and is exemplified by two discrete continuous phases that are each connected throughout the entire volume of the material (for example with a sponge, with phases of cellulose and air; in the hydrogel, this is comprised of gelatin and hyaluronic acid) resulting in a dizzying array of patterns that dramatically increase the surface area inside the material.
To test the hydrogel’s efficacy, Xu and her collaborators — including co-advisor Jason Burdick, formerly the Robert D. Bent Professor in Bioengineering at Penn Engineering and now the Bowman Endowed Professor at the University of Colorado Boulder, and the paper’s other senior author — first created several different versions of the hydrogel to find the sweet spot at which the constituents formed the bicontinuous structure and had the highest internal surface area. “We found that a precise combination of the various hydrogel components and control over their mixing was needed to form the bicontinuous structure,” says Burdick.
Read the full story in Penn Engineering Today.







 Speaker:
Speaker: 