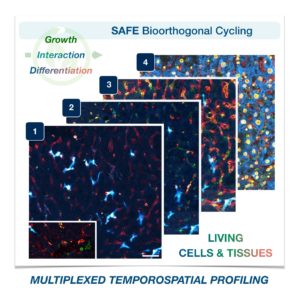
Akin to the packages sent from one person to another via an elaborate postal system, cells send tiny parcels that bear contents and packaging material that serve key purposes: To protect the contents from the outside world and to make sure it gets to the right place via a label with an address.
These packages are known as extracellular vesicles (EVs)—lipid-bound molecules that serve a variety of regulatory and maintenance functions throughout the body. They assist in the removal of unwanted materials within the cell, and they transport proteins, aid in DNA and RNA transfer, and promote tumorigeneses in cancerous cells.
Given their myriad roles, EVs have taken center stage for many researchers in the biomedical space as they have the potential to improve current methods of disease detection and treatment. The main challenge, however, is accurately identifying the molecular contents of EVs while also characterizing the EVs, which, unlike other cellular components that are more homogenous, have more heterogeneity.
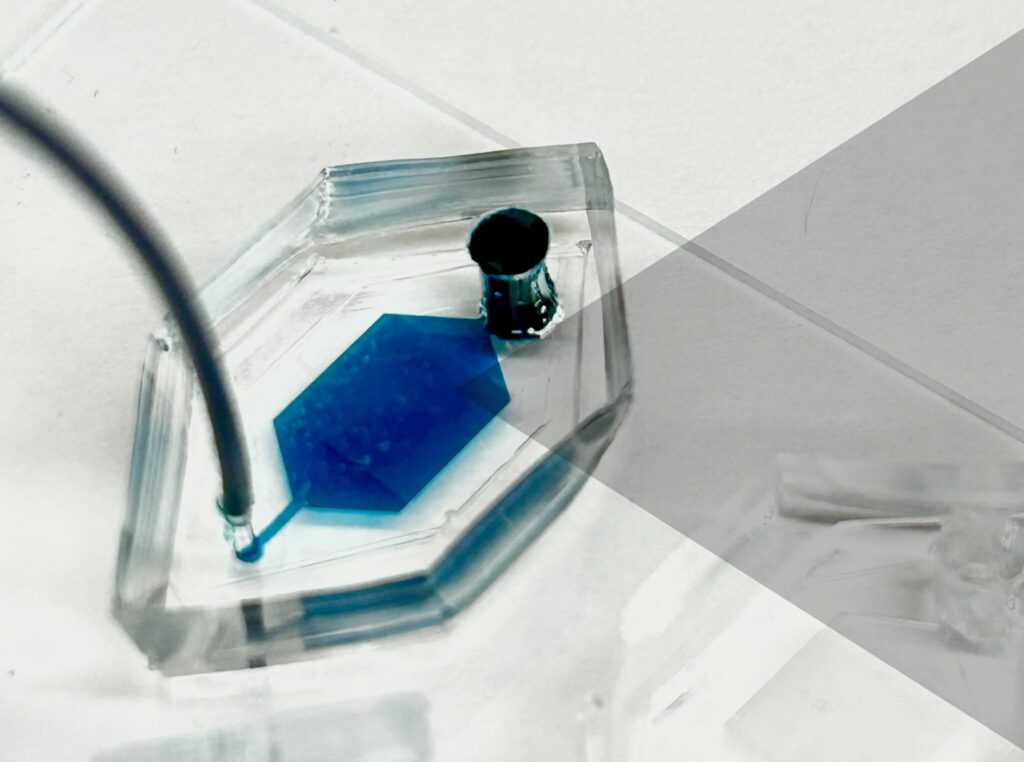
Now, a team of researchers at the University of Pennsylvania has developed a novel platform, droplet-free double digital assay, for not only profiling individual EVs but also accurately discerning their molecular contents. The researchers took the digital assay, which quantifies the contents of a molecule via binary metric—a 1 corresponds to the presence of a molecule and a zero to the lack thereof—and applies it to the EV. The work is published in Advanced Science.
The team was led by Jina Ko, an assistant professor with appointments in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and Perelman School of Medicine. “Our method allows for highly accurate quantification of the individual molecules inside an EV,” Ko says . “This opens up many doors in the realm of early disease detection and treatment.”
The researchers first compartmentalized individual EVs utilizing a microwell approach to isolate the EVs. Next, they captured individual molecules within the EVs and amplified the signal for clarity. The team then was able to determine the expression levels of pivotal EV biomarkers with remarkable precision via fluorescence.
Read the full story in Penn Today.
Jina Ko is an assistant professor in the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine in the Perelman School of Medicine and an assistant professor in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of Pennsylvania.
David Reynolds is a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Bioengineering in Penn Engineering.
Other authors include, Menghan Pan, George Galanis, Yoon Ho Roh, Renee-Tyler T. Morales, Shailesh Senthil Kumar, and Su-Jin Heo of the Department of Bioengineering at Penn Engineering; Jingbo Yang and Xiaowei Xu of the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Penn Medicine; and Wei Guo of the Department of Biology in the School of Arts & Sciences at Penn.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health: grants R00CA256353, R35 GM141832, and CA174523 (SPORE).



 Carlos Armando Aguila, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center of Neuroengineering and Therapeutics, advised by
Carlos Armando Aguila, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center of Neuroengineering and Therapeutics, advised by  Joseph Lance Victoria Casila is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of
Joseph Lance Victoria Casila is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of  Trevor Chan is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of
Trevor Chan is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of  Rakan El-Mayta is an incoming Ph.D. student in the lab of
Rakan El-Mayta is an incoming Ph.D. student in the lab of  Austin Jenk is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Austin Jenk is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Jiageng Liu is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Jiageng Liu is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Alexandra Neeser is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Alexandra Neeser is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  William Karl Selboe Ojemann, a Ph.D. Student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center for Neuroengineering and Therapeutics directed by
William Karl Selboe Ojemann, a Ph.D. Student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center for Neuroengineering and Therapeutics directed by  Savan Patel (BSE Class of 2023) conducted research in the lab of
Savan Patel (BSE Class of 2023) conducted research in the lab of  David E. Reynolds, a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of
David E. Reynolds, a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of  Andre Roots is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Andre Roots is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Emily Sharp, a second year Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of
Emily Sharp, a second year Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of  Nat Thurlow is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Nat Thurlow is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Maggie Wagner, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member in the labs of
Maggie Wagner, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member in the labs of