by Katherine Sas
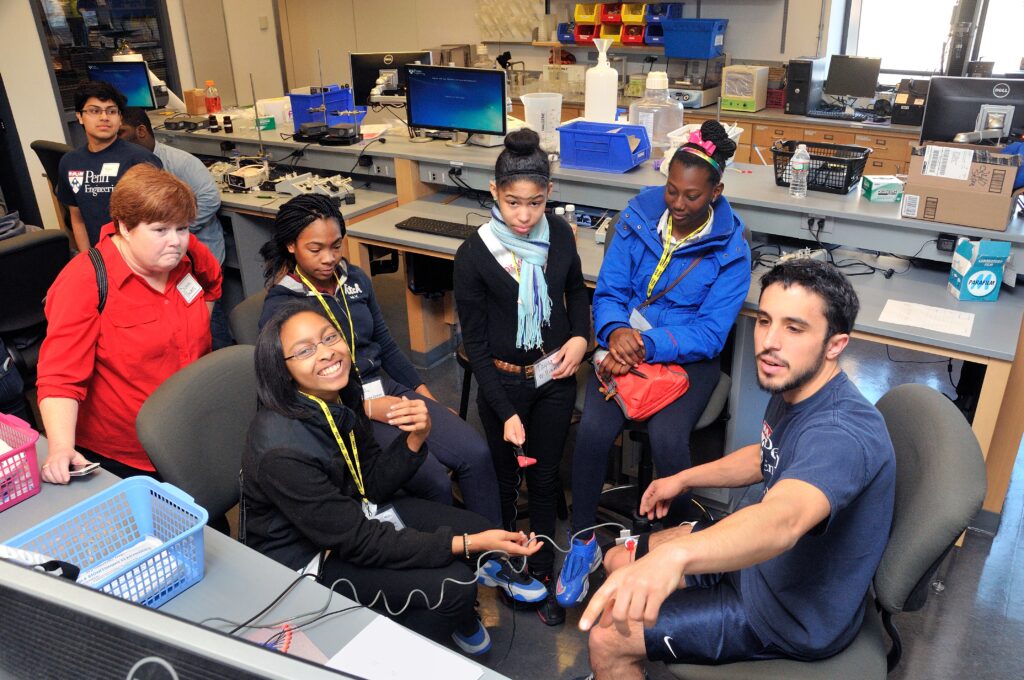

Last year marked not just the 50th anniversary of the Department of Bioengineering (BE) but the 10th anniversary of Bioengineer-Teach-Aspire (BETA) Day, one of the most beloved and impactful programs run by the Graduate Association of Bioengineers (GABE).
BETA Day, an annual event in which a diverse group of Philadelphia middle school students learns about bioengineering and a variety of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) fields from BE graduate students, has grown into an institution, one whose impact no one could have foreseen.
GABE’s original goal was to provide social opportunities for BE graduate students. While this is still an important function of the group, in the mid-2010s, students and board members found themselves looking for opportunities to provide more formalized outreach and mentorship. They wanted to have an impact on Philadelphia and cultivate the next generation of bioengineers.
The Seeds of BETA Day
Benjamin Freedman, a principal investigator at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, and founder of biotech startup Limax Biosciences, earned his doctorate in Bioengineering in the lab of Louis Soslowsky, Fairhill Professor in the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery within the Perelman School of Medicine (PSOM) and in Bioengineering within the School of Engineering and Applied Science (Penn Engineering). Freedman played a key role in BETA Day’s founding.
In 2009, Freedman, then an undergraduate at the University of Rochester, attended a talk at the City College of New York (CCNY), which sparked his interest in mentorship. Sheldon Weinbaum, a Distinguished Professor in Biomedical and Mechanical Engineering at CCNY and the Biomedical Engineering Society (BMES) inaugural diversity award winner, spoke about “fulfilling the dream” of mentorship and the struggle for inclusion in STEM fields, echoing the language of Martin Luther King Jr.
Inspired by this encounter, Freedman got involved with a mentorship program during his senior year. He later signed up for a lunch with Weinbaum to talk about mentorship. Freedman recalls that Weinbaum’s face “lit up” when he realized that this student didn’t just want to talk science but was genuinely interested in inclusion, diversity and mentorship.
Arriving at Penn Engineering and PSOM for graduate school in 2011, Freedman joined GABE, bringing this passion and experience with him and helping GABE to shape and clarify their outreach and mentorship programs.
From Campus to Community
Along with other GABE board members, such as Cori Riggin and Shauna Dorsey, Freedman worked over the course of a year and a half to identify the mentorship needs within BE and gauge student interest. David Meaney, Solomon R. Pollack Professor and then Chair of BE, and former BE faculty Susan Margulies, now Professor in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University, were particularly involved in these discussions.
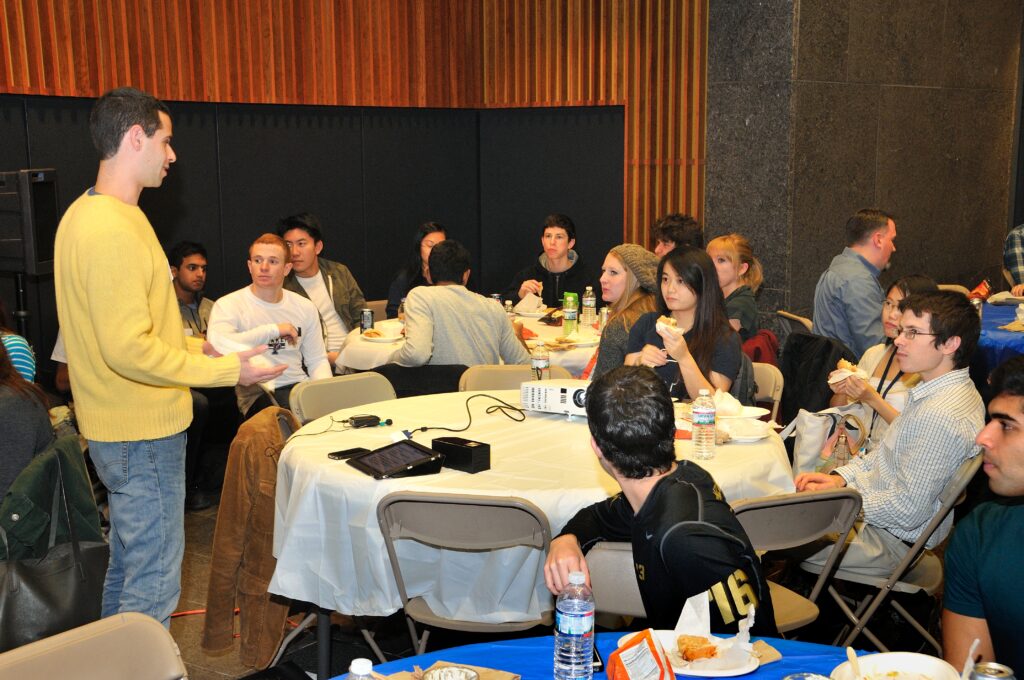

The GABE board reorganized to include mentorship and outreach chairs, and eventually started a formal mentorship program in partnership with the Penn undergraduate Biomedical Engineering Society (BMES). The mentorship program continues to this day, creating opportunities for BE graduate students to engage with undergraduate concerns through one-on-one meetings to discuss career or graduate school advice, summer BBQ’s, roundtable discussions and monthly meetups.
With an internal mentorship program established, the team turned their focus to Philadelphia. Initially, GABE established a partnership with iPraxis, a local STEM education non-profit, to do some outreach activities in middle schools. This partnership resulted in an Outstanding Outreach Award from the national Biomedical Engineering Society in 2014. But with the department’s 40th anniversary approaching, GABE’s members wanted to do something spectacular to celebrate and give back to the community.
Service Learning in Action
By then, Ocek Eke, Director of Graduate Students Programming at Penn Engineering, had been recently appointed Director of Global and Local Service Learning Programs. Eke provided Freedman and GABE advice on setting up effective outreach programs and to determine what resources the School could contribute. “We have a role to play to fulfill our mission,” Eke says, citing Penn’s motto, “Leges Sine Moribus Vanae,” which translates to “Laws without morals are useless.”
GABE’s efforts were part of a “wave” of interest in outreach and community service in both the department and the School, Eke remembers, including the undergraduate group Access Engineering and several service learning courses which took students to Asia, Africa and Central America. He was impressed by the lack of cynicism in the BE student body. “These are students who saw a need, who are passionate about what they want to achieve. They could have just been comfortable but were willing to go and stick their necks out. They used the resources we have here in Penn Engineering to address these needs.”
A (BETA) Day to Remember
The first BETA Day took place at the Singh Center for Nanotechnology, which had only just opened. Held with the enthusiastic participation of around 70 middle schoolers, and almost as many volunteers, the event included a full day of programming, with representation from every Penn Engineering department. There were science talks, workshops, and even a drone demo with Vijay Kumar, Nemirovsky Family Dean of Penn Engineering. The entire day was student-driven and staffed by volunteers, demonstrating the students’ commitment to making a difference.
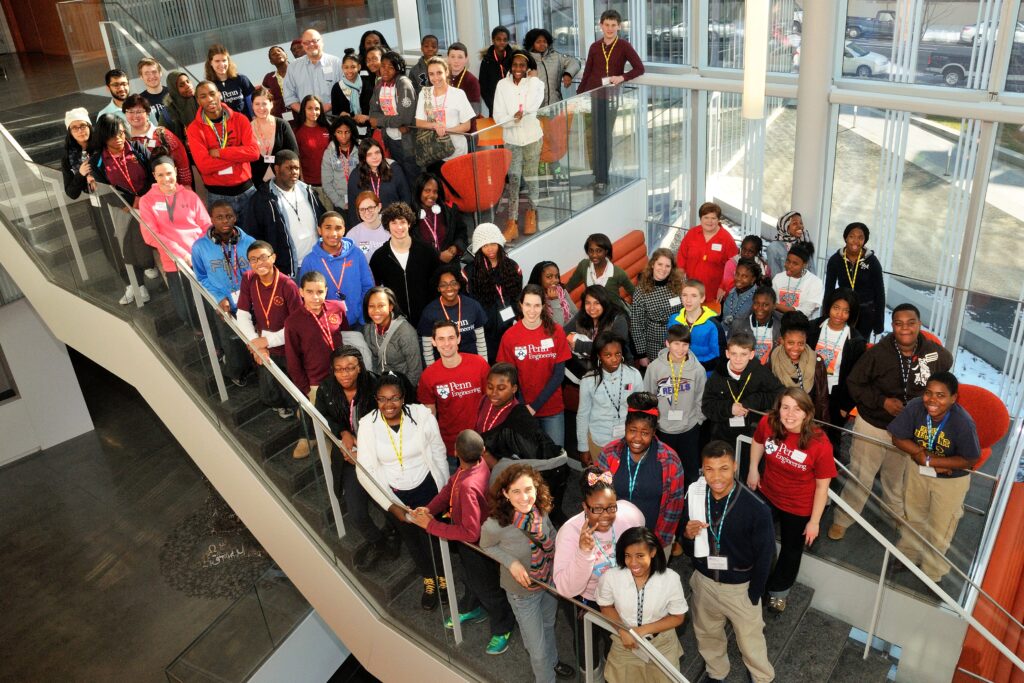

GABE never imagined BETA Day as an annual event, but the first instance was so successful, it became hard to imagine not repeating it. Ten years later, the GABE board continues to introduce bioengineering to a diverse and ambitious group of middle schoolers every spring.
In recent years, the location has shifted to other venues, including Pennovation Works, in Gray’s Ferry, and BE’s own education lab, the George H. Stephenson Foundation Educational Laboratory & Bio-MakerSpace. Penn’s General Robotics, Automation, Sensing and Perception (GRASP) Lab has also become a key collaborator in BETA Day.
In 2021, during the COVID-19 lockdown, the industrious and creative GABE board even tailored BETA Day activities to be held in an entirely virtual environment. “These types of events are not as successful when they’re only initiated by faculty,” says Freedman. Generating and sustaining student involvement has been a cornerstone of BETA Day’s continued success.
The Legacy of BETA Day
GABE’s mentorship efforts have grown as well, changing to meet evolving student needs. The mentorship program now involves students being placed in “families” of around four undergraduates and two graduate students, spanning a range of class years and experience levels. A third student association, the Master’s Association in Bioengineers (MAB), was established to better foster community and facilitate opportunities for master’s students.
The department also launched an applicant support program in 2020, enhancing BE’s mission of increasing diversity, equity and inclusion by pairing Ph.D. applicants to current doctoral students, who serve as mentors to help navigate the admissions process, giving feedback on application materials and providing other support to prospective students.
Structures of support and outreach activities like BETA Day have become a key emphasis of the department’s graduate student recruitment, helping to attract students who value the department’s core mission and increasing opportunities for underserved or underrepresented communities.
The legacy of that original BETA Day also continues in Freedman’s Lab. After graduating in 2017, having served on the GABE board and as President from 2015-2016, Freedman continued to mentor over 20 students during his postdoctoral research at Harvard. He is now building his own independent lab where diversity, mentorship and outreach are foundational pillars.
A Nebula of Inspiration
Perhaps the most consequential impact of BETA Day is the impression it makes on the middle schoolers who participate each year. “To really get to know what happens on BETA Day and what it’s true impact is, you need to experience it,” says Ravi Radhakrishnan, Herman P. Schwan Chair of the Department of Bioengineering and Professor in Bioengineering and in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering.
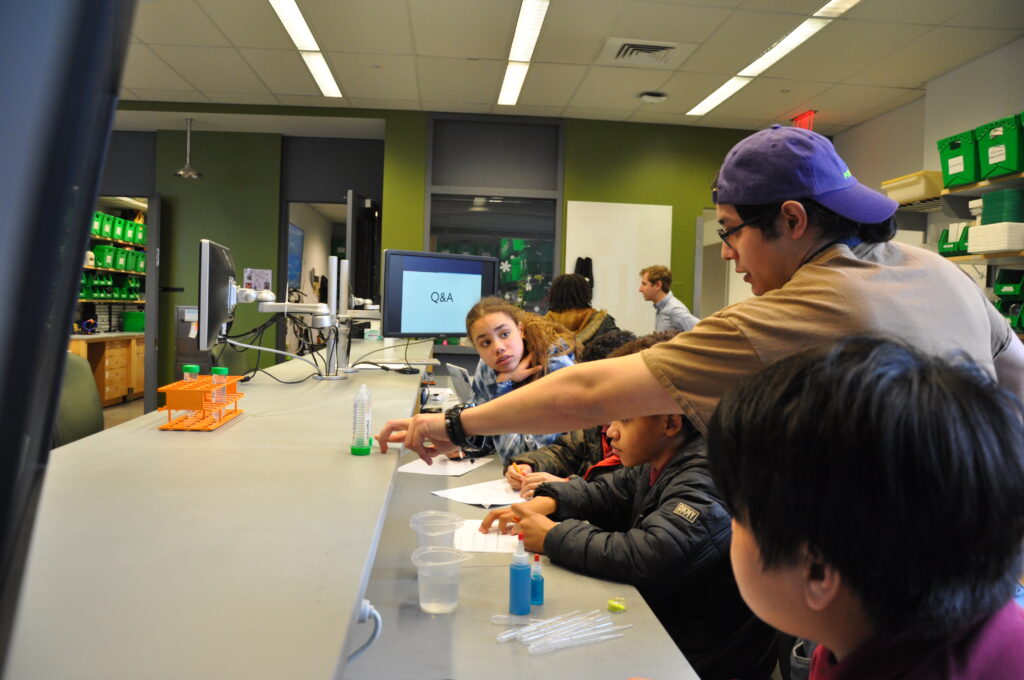

“I walked into the Stephenson Foundation Education Lab during BETA Day 2024,” recalls Radhakrishnan, “and what I saw was teams of teenagers tinkering with pipes that were clogged, strategizing on unclogging them without damaging them: an assignment that got them thinking in teams about how to prevent heart attacks.
“Expose these young minds to design thinking, versatile tools, and critical problems in biomedical engineering, and the elegant solutions they brainstorm are truly mind blowing. BETA Day is like the nebula where future biomedical stars are born.”




 However, diversity extends well beyond gender. For example, the National Research Mentoring Network (NRMN) has been working to increase diversity, including
However, diversity extends well beyond gender. For example, the National Research Mentoring Network (NRMN) has been working to increase diversity, including