by Sophie Burkholder
Tulane Researchers Use Cancer Imaging Technique to Help Detect Preeclampsia
 Preeclampsia is potentially life-threatening pregnancy disorder that typically occurs in about 200,000 expectant mothers every year. With symptoms of high blood pressure, swelling of the hands and feet, and protein presence in urine, preeclampsia is usually treatable if diagnosed early enough. However, current methods for diagnosis involve invasive procedures like cordocentesis, a procedure which takes a sample of fetal blood.
Preeclampsia is potentially life-threatening pregnancy disorder that typically occurs in about 200,000 expectant mothers every year. With symptoms of high blood pressure, swelling of the hands and feet, and protein presence in urine, preeclampsia is usually treatable if diagnosed early enough. However, current methods for diagnosis involve invasive procedures like cordocentesis, a procedure which takes a sample of fetal blood.
Researchers at Tulane School of Medicine led by assistant professor of bioengineering Carolyn Bayer, Ph.D., hope to improve diagnostics for preeclampsia with the use of spectral photoacoustic imaging. Using this technique, Bayer’s team noticed a nearly 12 percent decrease in placental oxygenation in rats with induced preeclampsia when compared to normal pregnant rats after only two days. If success in using this imaging technology continues at the clinical level, Bayer plans to find more applications of it in the detection and diagnosis of breast and ovarian cancers as well.
New CRISPR-powered device detects genetic mutations in minutes
Two groups of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley and the Keck Graduate Institute of the Claremont Colleges recently collaborated to design what they call a “CRISPR-Chip” – a combination of the CRISPR-Cas9 System with a graphene transistor to sequence DNA for the purpose of genetic mutation diagnosis. While companies like 23andMe made genetic testing and analysis more common and accessible for the general public in recent years, the CRISPR-Chip looks to streamline the technology even more.
This new chip eliminates the long and expensive amplification process involved in the typical polymerase chain reaction (PCR) used to read DNA sequences. In doing so, the CRISPR-Chip is much more of a point-of-care diagnostic, having the ability to quickly detect a given mutation or sequence when given a pure DNA sample. Led by Kiana Aran, Ph.D., the research team behind the CRISPR-Chip hopes that this new combination of nanoelectronics and modern biology will allow for a new world of possibilities in personalized medicine.
New Method of Brain Stimulation Might Alleviate Symptoms of Depression
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders in the United States, with nearly 3 million cases every year. For most patients suffering from depression, treatment involves prolonged psychotherapy, antidepressant medication, or even electroconvulsive therapy in extreme cases. Now, scientists at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine study the use of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) to alleviate symptoms of depression.
Led by Flavio Frohlich, Ph.D., who has an adjunct appointment in biomedical engineering, this team of researchers based this new solution on information from each patient’s specific alpha oscillations, which are a kind of wave that can be detected by an electroencephalogram (EEG). Those who suffer from depression tend to have imbalanced alpha oscillations, so Frohlich and his team sought to use tACS to restore this balance in those patients. After seeing positive results from data collected two weeks after patients in a clinical trial receives the tACS treatment, Frohlich hopes that future applications will include treatment for even more mental health disorders and psychiatric illnesses.
University of Utah Researchers Receive Grant to Improve Hearing Devices for Deaf Patients
Engineers at the University of Utah are part of team that recently received a $9.7 million grant from the National Institute of Health (NIH) to design new implantable hearing devices for deaf patients, with the hope to improve beyond the sound quality of existing devices. The work will build upon a previous project at the University of Utah called the Utah Electrode Array, a brain-computer interface originally developed by Richard Normann, Ph.D., that can send and receive neural impulses to and from the brain. This new device will differ from a typical cochlear implant because the Utah Electrode Array assembly will be attached directly to the auditory nerve instead of the cochlea, providing the patient with a much higher resolution of sound.
People & Places
Vivek Shenoy, Eduardo D. Glandt President’s Distinguished Scholar in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Secondary Faculty in Bioengineering, has been named the recipient of the 2018–19 George H. Heilmeier Faculty Award for Excellence in Research for “for pioneering multi-scale models of nanomaterials and biological systems.”
The Heilmeier Award honors a Penn Engineering faculty member whose work is scientifically meritorious and has high technological impact and visibility. It is named for George H. Heilmeier, a Penn Engineering alumnus and advisor whose technological contributions include the development of liquid crystal displays and whose honors include the National Medal of Science and Kyoto Prize.
Read the rest of the story on Penn Engineering’s Medium blog.
We would also like to congratulate Jay Goldberg, Ph.D., from Marquette University on his election as a fellow to the National Academy of Inventors. Nominated largely for his six patents involving medical devices, Goldberg also brings this innovation to his courses. One in particular called Clinical Issues in Biomedical Engineering Design allows junior and senior undergraduates to observe the use of technology in clinical settings like the operating room, in an effort to get students thinking about how to improve the use of medical devices in these areas.

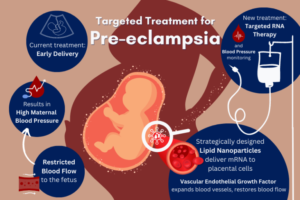 In one of the first studies of its kind, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, Michael Mitchell, J. Peter and Geri Skirkanich Assistant Professor of Innovation in Bioengineering, and Kelsey Swingle, Ph.D. student in the Mitchell Lab and lead author, describe their development of an LNP with the ability to target and deliver mRNA to trophoblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells in the placenta.
In one of the first studies of its kind, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, Michael Mitchell, J. Peter and Geri Skirkanich Assistant Professor of Innovation in Bioengineering, and Kelsey Swingle, Ph.D. student in the Mitchell Lab and lead author, describe their development of an LNP with the ability to target and deliver mRNA to trophoblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells in the placenta.
 Preeclampsia is potentially life-threatening pregnancy disorder that typically occurs in about 200,000 expectant mothers every year. With symptoms of high blood pressure, swelling of the hands and feet, and protein presence in urine, preeclampsia is usually treatable if diagnosed early enough. However, current methods for diagnosis involve invasive procedures like cordocentesis, a procedure which takes a sample of fetal blood.
Preeclampsia is potentially life-threatening pregnancy disorder that typically occurs in about 200,000 expectant mothers every year. With symptoms of high blood pressure, swelling of the hands and feet, and protein presence in urine, preeclampsia is usually treatable if diagnosed early enough. However, current methods for diagnosis involve invasive procedures like cordocentesis, a procedure which takes a sample of fetal blood.