by Sophie Burkholder
New 3D Tumor Models Could Improve Cancer Treatment
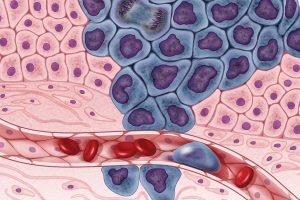 New ways of testing cancer treatments may now be possible thanks to researchers at the University of Akron who developed three-dimensional tumor models of triple-negative breast cancer. Led by Dr. Hossein Tavana, Ph. D., an associate professor of biomedical engineering at the university, the Tissue Engineering Microtechnologies Lab recently received a $1.13 million grant from the prestigious National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institute of Health (NIH) to continue improving these tumor models. Tumors are difficult to fully replicate in vitro, as they are comprised of cancerous cells, connective tissue, and matrix proteins, among several other components. With this new grant, Tavana sees creating a high-throughput system that uses many identical copies of the tumor model for drug testing and better understanding of the way tumors operate. This high-throughput method would allow Tavana and his lab to isolate and test several different approaches at once, which they hope will help change the way tumors are studied and treated everywhere.
New ways of testing cancer treatments may now be possible thanks to researchers at the University of Akron who developed three-dimensional tumor models of triple-negative breast cancer. Led by Dr. Hossein Tavana, Ph. D., an associate professor of biomedical engineering at the university, the Tissue Engineering Microtechnologies Lab recently received a $1.13 million grant from the prestigious National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institute of Health (NIH) to continue improving these tumor models. Tumors are difficult to fully replicate in vitro, as they are comprised of cancerous cells, connective tissue, and matrix proteins, among several other components. With this new grant, Tavana sees creating a high-throughput system that uses many identical copies of the tumor model for drug testing and better understanding of the way tumors operate. This high-throughput method would allow Tavana and his lab to isolate and test several different approaches at once, which they hope will help change the way tumors are studied and treated everywhere.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Poses Greater Threat to Neural Processing
Even though we all know we probably shouldn’t listen to music at high volumes, most of us typically do it anyway. But researchers at Purdue University recently found that noise-induced hearing loss could cause significant changes in neural processing of more complex sound inputs. Led by Kenneth Henry, Ph.D., an assistant professor of otolaryngology at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and Michael Heinz, Ph.D., a professor of biomedical engineering at Purdue University, the study shows that when compared with age-related hearing loss, noise-induced hearing loss will result in a greater decrease in hearing perception even when the two kinds of hearing loss appear to be of the same degree on an audiogram. This is because noise-induced hearing loss occurs because of physical trauma to the ear, rather than the long-term electrochemical degradation of some components that come happen with age. The evidence of this research is yet another reason why we should be more careful about exposing our ears to louder volumes, as they pose a greater risk of serious damage.
Increasing the Patient Populations for Research in Cartilage Therapy and Regenration
Despite the great progress in research of knee cartilage therapy and regeneration, there are still issues with the patient populations that most studies consider. Researchers often want to test new methods on patients that have the greatest chance of injury recovery without complications – often referred to as “green knees” – but this leaves out those patient populations who suffer from conditions or defects that have the potential to cause complications – often referred to as “red knees.” In a new paper published in Regenerative Medicine, the Mary Black Ralston Professor for Education and Research in Orthopaedic Surgery and secondary faculty in the Department of Bioengineering at Penn, Robert Mauck, Ph.D., discusses some cartilage therapies that may be suitable for red knee populations.
Working with James Carey, M.D., the Director of the Penn Center for Cartilage Repair and Osteochondritis, Mauck and his research team realized that even those with common knee cartilage conditions such as the presence of lesions or osteoarthritis were liable to be excluded from most regeneration studies. In discussing alternatives methods and structures of studying cartilage repair and regeneration, Mauck and Carey hope that future therapies will be applicable to a wider range of patient populations, and that there will soon be more options beyond full joint replacement for those with red knee conditions.
Plant-Like Superhydrophobicity Has Applications in Biomedical Engineering
Researchers in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University recently found ways of incorporating the superhydrophobic properties of some plant leaves into biomedical applications through what they’re calling a “lotus effect.” The Gaharwar Lab, led by principal investigator and assistant professor of biomedical engineering Akhilesh Gaharwar, Ph.D., developed an assembly of two-dimensional atomic layers that they describe as a “nanoflower” to help control surface wetting in a biomedical setting. A recent paper published in Chemical Communications describes Gaharwar and his team’s work as expanding the use of superhydrophobic surface properties in biomedical devices by demonstrating the important role that atomic vacancies play in the wetting characteristic. While Gaharwar hopes to research the impact that controlling superhydrophobicity could have in stem cell applications, his work already allows for innovations in self-cleaning and surface properties of devices involving labs-on-a-chip and biosensing.
People and Places
Nader Engheta, H. Nedwill Ramsey Professor in Electrical and Systems Engineering, Bioengineering and Materials Science and Engineering, has been inducted into the Canadian Academy of Engineering (CAE) as an International Fellow. The CAE comprises many of Canada’s most accomplished engineers and Engheta was among the five international fellows that were inducted this year.
The Academy’s President Eddy Isaacs remarked: “Over our past 32 years, Fellows of Academy have provided insights in the fields of education, infrastructure, and innovation, and we are expecting the new Fellows to expand upon these contributions to public policy considerably.”
Read the full story on Penn Engineering’s Medium Blog.
We would like to congratulate Anthony Lowman, Ph.D., on his appointment as the Provost and Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs at Rowan University. Formerly the Dean of Rowan’s College of Engineering, Lowman helped the college double in size, and helped foster a stronger research community. Lowman also helped to launch a Ph.D. program for the school, and added two new departments of Biomedical Engineering and Experiential Engineering Education in his tenure as the dean. Widely recognized for his research on hydrogels and drug delivery, Lowman was also formerly a professor of bioengineering at Temple University and Drexel University.
Lastly, we would like to congratulate Daniel Lemons, Ph.D., on his appointment as the Interim President of Lehman College of the City University of New York. Lemons, a professor in the Department of Biology at City College, specializes in cardiovascular and comparative physiology, and was also one of the original faculty members of the New York Center for Biomedical Engineering. With prior research funded by both the National Institute of Health (NIH) and the National Science Foundation (NSF), Lemons also holds patents in biomechanics teaching models and mechanical heart simulators.

 New ways of testing cancer treatments may now be possible thanks to researchers at the University of Akron who developed three-dimensional tumor models of triple-negative breast cancer. Led by
New ways of testing cancer treatments may now be possible thanks to researchers at the University of Akron who developed three-dimensional tumor models of triple-negative breast cancer. Led by