by Melissa Pappas
The rise of drug-resistant bacteria infections is one of the world’s most severe global health issues, estimated to cause 10 million deaths annually by the year 2050. Some of the most virulent and antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens are the leading cause of life-threatening, hospital-acquired infections, particularly dangerous for immunocompromised and critically ill patients. Traditional and continual synthesis of antibiotics will simply not be able to keep up with bacteria evolution.
To avoid the continual process of synthesizing new antibiotics to target bacteria as they evolve, Penn Engineers have looked at a new, natural resource for antibiotic molecules.

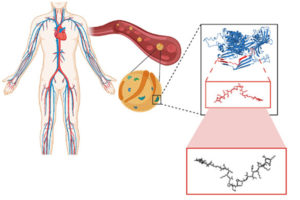
A recent study on the search for encrypted peptides with antimicrobial properties in the human proteome has located naturally occurring antibiotics within our own bodies. By using an algorithm to pinpoint specific sequences in our protein code, a team of Penn researchers along with collaborators, led by César de la Fuente, Presidential Assistant Professor in Psychiatry, Bioengineering, Microbiology, and Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Marcelo Torres, a post doc in de la Fuente’s lab, were able to locate novel peptides, or amino acid chains, that when cleaved, indicated their potential to fend off harmful bacteria.
Now, in a new study published in ACS Nano, the team along with Angela Cesaro, the lead author and post doc in de la Fuente’s lab, have identified three distinct antimicrobial peptides derived from a protein in human plasma and demonstrate their abilities in mouse models. Angela Cesaro performed a great part of the activities during her PhD under the supervision of corresponding author, Professor Angela Arciello, from the University of Naples Federico II. The collaborative study also includes Utrecht University in the Netherlands.
“We identified the cardiovascular system as a hot spot for potential antimicrobials using an algorithmic approach,” says de la Fuente. “Then we looked closer at a specific protein in the plasma.”
Read the full story in Penn Engineering Today.

