In the ever-evolving battle against cancer, immunotherapy presents a turning point. It began with harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer, a concept rooted more than a century ago but only gaining significant momentum in recent years. Pioneering this shift were therapies like CAR T cell therapy, which reprograms a patient’s T cells to attack cancer cells. Within this domain, bispecific T cell engagers, or bispecific antibodies, have emerged as effective treatments for many blood-borne cancers in the clinic and are being evaluated for solid tumor therapy.
These antibodies simultaneously latch onto both a cancer cell and a T cell, effectively bridging the gap between the two. This proximity triggers the T cells to unleash their lethal arsenal, thereby killing the cancer cells. However, bispecific T cell engagers, like many cancer therapies, face hurdles such as cell-specific targeting limitations, known as on-target off-tumor toxicity, which means the tumor is correctly targeted but so are other healthy cells in the body, leading to healthy tissue damage. Moreover, bispecific antibodies may also lead to immune system overactivation, a precursor for cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and neurotoxicity.
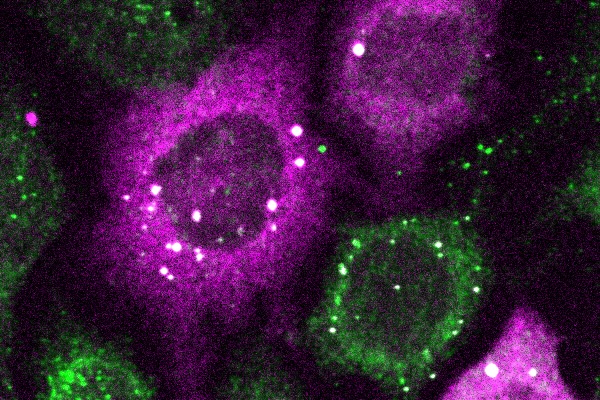
Now, researchers led by Michael Mitchell of the University of Pennsylvania have found a way to circumvent many of these deleterious effects by developing a bispecific T cell nanoengager that is equipped with an “off switch.” Their findings are published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“We’re excited to show that bispecific antibodies can be tweaked in a way that allows us to tap into their powerful cancer-killing potential without inducing toxicity to healthy tissues,” says Mitchell, associate professor of bioengineering at Penn’s School of Engineering and Applied Science. “This new controllable drug-delivery mechanism, which we call switchable bispecific T cell nanoengagers, or SiTEs, adds this switchable component to the antibody via administering an FDA-approved small-molecule drug, amantadine.”
Read the full story in Penn Today.