by Nathi Magubane
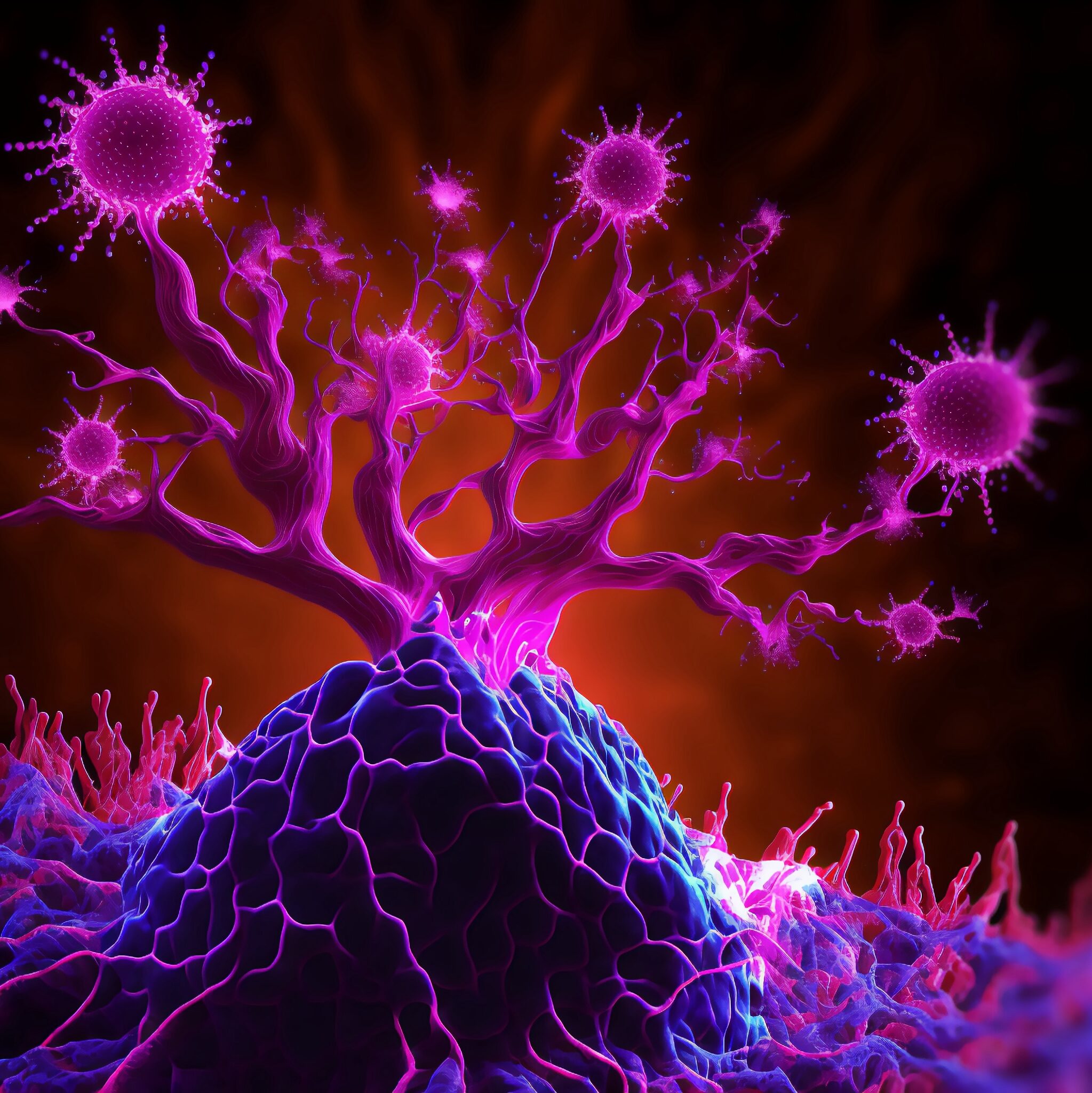
The tumor microenvironment—an ad hoc, messy amalgamation of signaling molecules, immune cells, fibroblasts, blood vessels, and the extracellular matrix—acts like a “powerful security system that protects solid tumors from invaders seeking to destroy them,” says Michael Mitchell, a bioengineer at the University of Pennsylvania working on nanoscale therapeutics aimed at targeting cancers.
“A lot like the Death Star with its surrounding fleet of fighter ships and protective shields, solid tumors can use features like immune cells and vasculature to exert force, acting as a physical barrier to rebel forces (nanoparticles) coming in to deliver the payload that destroys it,” Mitchell says.
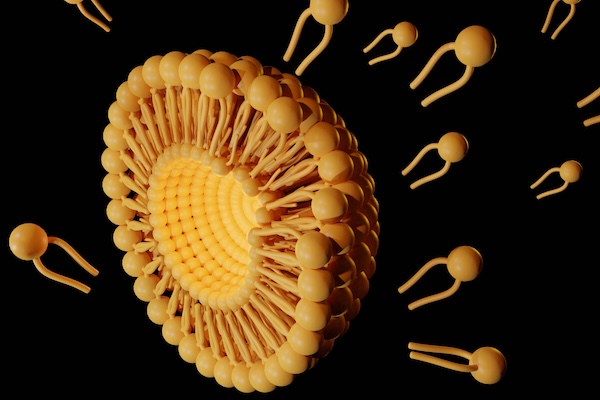
Now, researchers in the Mitchell lab have teamed up with Wei Guo’s group in the School of Arts & Sciences at Penn and Drew Weissman of the Perelman School of Medicine to figure out the molecular mechanisms that make tumor microenvironments seemingly impenetrable and found that small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are secreted by tumor cells and act as a “forcefield,” blocking therapeutics. Their findings are published in Nature Materials.
“This discovery reveals how tumors create a robust defense system, making it challenging for nanoparticle-based therapies to reach and effectively target cancer cells,” Guo says. “By understanding the cellular mechanisms driving these responses, we can potentially develop strategies to disable this defense, allowing therapeutics to penetrate and attack the tumor more efficiently.”
The research builds on a prior collaboration between Guo and Mitchell’s labs, wherein the teams focused on how tumor-associated immune cells, known as macrophages, contribute to the suppression of anti-tumor immunity by secreting extracellular vesicles.
Read the full story in Penn Today.
Michael Mitchell is an associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and director of the Lipid Nanoparticle Synthesis Core at the Penn Institute for RNA Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania.
Wei Guo is the Hirsch Family President’s Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biology in Penn’s School of Arts & Sciences.
Ningqiang Gong, a former postdoctoral researcher in the Mitchell lab at Penn Engineering, is an assistant professor at the University of Science and Technology of China.
Wenqun Zhong is a reseearch associate in the Guo Laboratory in Penn Arts & Sciences.
Other authors include: Alex G Hamilton, Dongyoon Kim, Junchao Xu, and Lulu Xue of Penn Engineering; Junhyong Kim, Zhiyuan Qin, and Fengyuan Xu of Penn Arts & Sciences; Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh and Drew Weissman of the Perelman School of Medicine; Andrew E. Vaughn and Gan Zhao of the Penn School of Veterinary Medicine; Jinghong Li and Xucong Teng of the University of Beijing; and Xing-Jie Liang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
This research received support from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (DP2 TR002776, R35 GM141832, and NCI P50 CA261608), Burroughs Wellcome Fund, U.S. National Science Foundation CAREER Award (CBET-2145491), and an American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant (RGS-22-1122-01-ET.)







 Carlos Armando Aguila, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center of Neuroengineering and Therapeutics, advised by
Carlos Armando Aguila, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center of Neuroengineering and Therapeutics, advised by  Joseph Lance Victoria Casila is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of
Joseph Lance Victoria Casila is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of  Trevor Chan is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of
Trevor Chan is a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering in the lab of  Rakan El-Mayta is an incoming Ph.D. student in the lab of
Rakan El-Mayta is an incoming Ph.D. student in the lab of  Austin Jenk is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Austin Jenk is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Jiageng Liu is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Jiageng Liu is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Alexandra Neeser is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Alexandra Neeser is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  William Karl Selboe Ojemann, a Ph.D. Student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center for Neuroengineering and Therapeutics directed by
William Karl Selboe Ojemann, a Ph.D. Student in Bioengineering, is a member of the Center for Neuroengineering and Therapeutics directed by  Savan Patel (BSE Class of 2023) conducted research in the lab of
Savan Patel (BSE Class of 2023) conducted research in the lab of  David E. Reynolds, a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of
David E. Reynolds, a Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of  Andre Roots is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Andre Roots is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Emily Sharp, a second year Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of
Emily Sharp, a second year Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member of the lab of  Nat Thurlow is a Ph.D. student in the lab of
Nat Thurlow is a Ph.D. student in the lab of  Maggie Wagner, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member in the labs of
Maggie Wagner, Ph.D. student in Bioengineering, is a member in the labs of