After a year of hybrid learning, Penn Bioengineering (BE) seniors were excited to return to the George H. Stephenson Foundation Educational Laboratory & Bio-MakerSpace for Senior Design (BE 495 & 496), a two-semester course in which students work in teams to conceive, design and pitch their capstone projects in bioengineering. This year’s projects include tools for monitoring health, software to improve communication for the healthcare and supply chain industries, and devices to improve patient care for women and underrepresented minorities.
After a year of hybrid learning, Penn Bioengineering (BE) seniors were excited to return to the George H. Stephenson Foundation Educational Laboratory & Bio-MakerSpace for Senior Design (BE 495 & 496), a two-semester course in which students work in teams to conceive, design and pitch their capstone projects in bioengineering. This year’s projects include tools for monitoring health, software to improve communication for the healthcare and supply chain industries, and devices to improve patient care for women and underrepresented minorities.
The year culminated in the annual Senior Design Expo on April 13 in the Singh Center for Nanotechnology, in which the students presented their pitches to a panel of alumni judges, followed by demonstrations in the George H. Stephenson Foundation Educational Laboratory & Bio-MakerSpace which were open to the entire Penn community. This year’s winners of the Bioengineering Senior Design Competition were teams Chrysalis, Modulo Prosthetics, and ReiniSpec.

The three winning teams went on to compete in the annual interdepartmental Senior Design Competition sponsored by the Penn Engineering Alumni Society. BE took home two of the four interdepartmental awards: Team Modulo Prosthetics won the “Technology and Innovation Prize,” recognizing the project which best represents the highest and best use of technology and innovation to leverage engineering principles; and Team ReiniSpec won the “Leadership Prize,” which recognizes the team which most professionally and persuasively presents their group project to incorporate a full analysis of their project scope, advantages, and challenges, and addresses the commercialization and future potential of their research.
All BE teams were also required to submit their projects to local and national competitions, and were met with resounding success. “The creativity and accomplishment of this Senior Design class is really unparalleled,” said David Meaney, Solomon R. Pollack Professor in Bioengineering, Senior Associate Dean of Penn Engineering, and instructor for Senior Design. “The number of accolades received by these students, as well as the interest in transforming their ideas into real products for patients, reached a new level that makes us extremely proud.”
Keep reading for a full list of this year’s projects and awards.
Team 1 – MEViD
MEViD (Multichannel Electrochemical Viral Diagnostic) is a modular, low cost device that leverages electrochemistry to rapidly diagnose viral diseases from saliva samples.
Team members: Yuzheng (George) Feng, Daphne Kontogiorgos-Heintz, Carisa Shah, Pranshu Suri, & Rachel Zoneraich
- Second Place at the 2022 M&T Summit
- Finalist at the Design of Medical Devices Conference at the University of Minnesota
- Finalist for the Global Health Track of the 2022 Johns Hopkins Healthcare Design Competition
Team 2 – MOD EZ-IO
MOD EZ-IO is a low-cost, novel intraosseous drill that uses force and RPM readings to alert the user via an LED when they have breached cortical bone and entered cancellous bone, guiding proper IO placement.
Team members: Gregory Glova, Kaiser Okyan, Patrick Paglia, Rohan Vemu, & Tshepo Yane
- Winner of a Berkman Opportunity Fund for 2022
Team 3 – Harvest by Grapevine
Harvest by Grapevine is a user-centric software solution that merges social network communication and supply chain logistics to connect hospitals and suppliers under one unified platform.
Team members: Nicole Bedanova, Kerry Blatney, Blake Grimes, Brenner Maull, & Lukas Yancopoulos
- Winner of the 2022 President’s Innovation Prize (team member Lukas Yancopoulos and partner William Kohler Danon [SAS 2022] for “Grapevine,” the larger software package of which “Harvest” was a part)
- Winner of the Weiss Tech House Innovation Fund
- Penn Wharton Innovation Fund Implementation Award Winner
- Semifinalist for the Venture Lab 2022 Startup Challenge;
- Finalist for the Pear Startup Competition
- Finalist for the Pear Accelerator
- Finalist for the Wharton MBA Fund Pitch Competition
- Finalist for the Digital Health Track of the 2022 Johns Hopkins Healthcare Design Competition
Team 4 – CliniCall
CliniCall helps streamline and centralize communication channels, offering a real-time monitoring device that enables on-site/attending physicians to communicate with on-call physicians through a livestream of patients and data.
Team members: Neepa Gupta, Santoshi Kandula, Sue Yun Lee, & Ronil Synghal
Team 5 – PneuSonus
PneuSonus is a low-cost, user-friendly wearable strap that aids in detecting pediatric pneumonia by using frequency analysis of sound waves transmitted through the lungs to identify specific properties related to fluid presence, a valid indicator specific to pneumonia.
Team members: Iman Hossain, Kelly Lopez, Sophia Mark, Simi Serfati, & Nicole Wojnowski
Team 6 – Chrysalis
Chrysalis is a smart swaddle system comprising an electric swaddle and accompanying iOS application that comforts neonatal abstinence syndrome infants via stochastic resonance and maternal heartbeat vibrational patterns to reduce opioid withdrawal symptoms without pharmacological intervention or constant nurse oversight as well as streamlines the Eat, Sleep, Console documentation process for nurses.
Team members: Julia Dunn, Rachel Gu, Julia Lasater, & Carolyn Zhang
- Bioengineering Senior Design competition winner
- People’s Choice Award for the Rice 360 Global Health Design competition
- Third Place in the Penn Nursing Innovation Accelerator Competition
- Finalist in the Advanced Health Track of the 2022 Johns Hopkins Healthcare Design Competition
Team 7 – EquitOx
EquitOx is a revolutionized fingertip pulse oximeter designed for EMS that addresses racial inequality in medicine through the use of one-off tongue-calibrated SpO2 measurements.
Team members: Ronak Bhagia, Estelle Burkhardt, Juliette Hooper, Caroline Smith, & Kevin Zhao
- Winner of a Berkman Opportunity Fund for 2022
Team 8 – Modulo Prosthetics
Modulo Prosthetic is an adjustable, low-cost, thumb prosthetic with integrated haptic feedback that attaches to the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of partial hand amputees and assists in activities of daily living (ADLs).
Team members: Alisha Agarwal, Michelle Kwon, Gary Lin, Ian Ong, & Zachary Spalding
- Bioengineering Senior Design competition winner
- Third Place in the Rice 360 Global Health Design Competition
- Venture Labs Penn Wharton Innovation Fund Validation Award
- Winner of the Technology and Innovation Prize at Penn Engineering’s Senior Design Competition
Team 9 – Cor-Assist By Cygno Technologies
COR-ASSIST by Cygno Technologies is a low-cost intra-aortic balloon enhancement that directly supports heart function by increasing cardiac output to 2.8L/min, at a much lower cost and bleeding risk than the current Impella cardiac assist device.
Team members: Francesca Cimino, Allen Gan, Shawn Kang, Kristina Khaw, & William Zhang
- Second Place in the Emerging Medical Innovation Valuation Competition at the University of Minnesota
- Winner of a Berkman Opportunity Fund for 2022
Team 10 – Pedalytics
Pedalytics Footwear is a rechargeable sandal that continuously monitors foot health and prevents diabetic foot ulcer formation by novelly tracking three key metrics indicative of ulceration, temperature, oxygen saturation, and pressure, and sending alerts to patients via the Pedalytics app when metric abnormalities are detected.
Team members: Samantha Brosler, Constantine Constantinidis, Quincy Hendricks, Ananyaa Kumar, & María José Suárez
- Finalist in the M&T Innovation Fund Competition
- Penn Wharton Innovation Fund Implementation Award Winner
- Winner of a Berkman Opportunity Fund for 2022
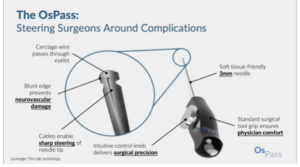
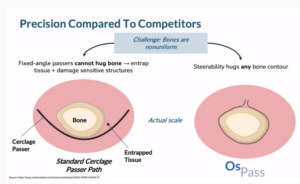
Team 11 – ReiniSpec
ReiniSpec is a redesigned speculum to improve the gynecological exam experience, increasing patient comfort with a silicone shell and using motorized arm adjustments to make it easily adjustable for each patient, while also incorporating a camera, lights, and machine learning to aid in better diagnosis by gynecologists.
Team members: Caitlin Frazee, Caroline Kavanagh, Ifeoluwa Popoola, Alexa Rybicki, & Michelle White
- Bioengineering Senior Design competition winner
- Winner of a Berkman Opportunity Fund for 2022
- Winner of the Leadership Prize at Penn Engineering’s Senior Design Competition
Learn more about the 2022 Senior Design projects, including full abstracts and photo gallery, on the Stephenson Bio-MakerSpace website.
Watch all the 2022 project pitches on the BE Labs Youtube channel 2022 Senior Design Playlist: