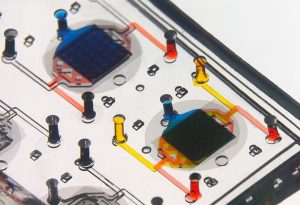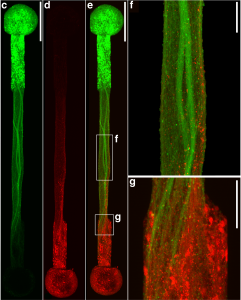
Connecting the human brain to electrical devices is a long-standing goal of neuroscientists, bioengineers, and clinicians, with applications ranging from deep brain stimulation (DBS) to treat Parkinson’s disease to more futuristic endeavors such as Elon Musk’s NeuraLink initiative to record and translate brain activity. However, these approaches currently rely on using implantable metallic electrodes that inherently provoke a lasting immune response due to their non-biological nature, generally complicating the reliability and stability of these interfaces over time. To address these challenges, D. Kacy Cullen, Associate Professor in Neurosurgery and Bioengineering, and Dayo Adewole, a doctoral candidate in Bioengineering, worked with a multi-disciplinary team of collaborators to develop the first “living electrodes” as an implantable, biological bridge between the brain and external devices. In a recent article published in Science Advances, the team demonstrated the fabrication of hair-like microtissue comprised of living neuronal networks and bundled tracts of axons — the signal sending fibers of the nervous system — protected within soft hydrogel cylinders. They showed that these axon-based living electrodes could be fully controlled and monitored with light — thus eliminating the need for electrical contact — and are capable of surviving and forming synapses with the brain as demonstrated in an adult rat model. While further advancements are necessary prior to clinical use, the current findings provide the foundation for a new class of “living electrodes” as a biological intermediary between humans and devices capable of leveraging natural mechanisms to potentially provide a stable interface for clinical applications.
Cullen has a primary appointment in the Department of Neurosurgery in the Perelman School of Medicine, with a secondary appointment in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science, and an appointment in the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center in Philadelphia.







 A recent study published in Science Translational Medicine announces a discovery which could halt cartilage degeneration caused by osteoarthritis: “These researchers showed that they could target a specific protein pathway in mice, put it into overdrive and halt cartilage degeneration over time. Building on that finding, they were able to show that treating mice with surgery-induced knee cartilage degeneration through the same pathway via the state of the art of nanomedicine could dramatically reduce the cartilage degeneration and knee pain.” This development could eventually lead to treating osteoarthritis with injection rather than more complicated surgery.
A recent study published in Science Translational Medicine announces a discovery which could halt cartilage degeneration caused by osteoarthritis: “These researchers showed that they could target a specific protein pathway in mice, put it into overdrive and halt cartilage degeneration over time. Building on that finding, they were able to show that treating mice with surgery-induced knee cartilage degeneration through the same pathway via the state of the art of nanomedicine could dramatically reduce the cartilage degeneration and knee pain.” This development could eventually lead to treating osteoarthritis with injection rather than more complicated surgery.
 A recent piece in the Daily Pennsylvanian highlights
A recent piece in the Daily Pennsylvanian highlights